| Lesson by Max Millard and Kevin Gortney for Presidio Middle School, 8th grade science, 4-19-07 | Adjust Background: Darker / Lighter |
If you've ever lain on your back in a swimming pool, you have demonstrated the ability of an object to float in water. You float because the water displaced by your body weighs the same as your body. In the pool, the water is pushing on your body's mass with a stronger force than gravity is pulling it down. This is called "positive" buoyancy, or the ability of an object to stay afloat. Simply put, if an object in water displaces its own weight in the water, the object will float. If the object is denser (heavier) than the water it displaces, it will sink (also known as "negative" buoyancy). Ships float because they are less dense than the surrounding water and so the force of gravity pulling on the ship is less than the force of water pushing the ship up. The term SALINITY or SALT CONTENT describes the concentration of salt in a given amount of water. Salinity is expressed in parts per thousand (ppt). This means one gram of salt mixed with 999 milliliters (almost 1 liter) of water is one part per thousand. The average salinity of ocean water is about 35 ppt ? that is, 35 grams of salt per liter, although it can fluctuate between 32 and 37 ppt, depending on how much freshwater is available. Freshwater normally has a salinity of less than 0.5 ppt. Brackish water, found where a river flows into the sea, can have a salinity as high as 17 ppt. Because most ocean water contains high amounts of dissolved minerals such as salt, it is more dense than freshwater, so objects in seawater will float higher and easier than they do in freshwater. Imagine the extra particles of minerals acting as "tiny little hands" pushing a ship up while gravity is pulling it down. The more "tiny little hands" there are to push the object up, the easier it is for the object to float. A ship holding a given amount of cargo will float high in seawater. When the ship arrives in less saline waters it will ride lower because there are less dissolved minerals in the water. The "Plimsoll mark" shows the maximum amount of cargo a ship can have in freshwater and seawater to ensure that a heavily loaded ship does not sink as it reaches freshwater.
F: Freshwater
B: Brackish Water
S: Saltwater
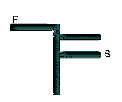 Plimsoll marks on ship
Plimsoll marks on ship
The Problem:
Captain Jack Sparrow does not believe the old wives' tale that a pirate ship heavily loaded with treasure and cargo will float lower in the water and possibly sink as it travels from the open ocean into a harbor at the mouth of river. You, being his trusty first mate, understand that something in the ocean water allows the ship to float better than if it was in freshwater. Your job is to convince the Captain that loading up in open ocean water and traveling towards the mouth of a river could mean death to the crew and the loss of all the buried treasure you have uncovered. Based on the background information you have about the relationship between salinity and buoyancy, conduct the following experiment to determine if salt concentration in water has an effect on the ability of an object of a specific mass to float (buoyancy).
I. Purpose: To investigate buoyancy by:
II. Materials
III. Procedure
Questions to Consider:
Directions: